 |
Baltimore MD (SPX) Jan 09, 2009 A mysterious flash of light from somewhere near or far in the universe is still keeping astronomers in the dark long after it was first detected by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope in 2006. It might represent an entirely new class of stellar phenomena that has previously gone undetected in the universe, say researchers. Astronomers commonly observe intense flashes of light from a variety of stellar explosions and outbursts, such as novae and supernovae. Hubble discovered the cosmic flash on February 21, 2006. It steadily rose in brightness for 100 days, and then dimmed back to oblivion after another 100 days. The rise and fall in brightness has a signature that simply has never been recorded for any other type of celestial event. Supernovae peak after no more than 70 days, and gravitational lensing events are much shorter. Therefore, this observation defies a simple explanation, reports Kyle Barbary of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) in Berkeley, Calif. He is describing the bizarre Hubble observation at the 213th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Long Beach, Calif. "We have never seen anything like it," he concludes. The spectral fingerprints of light coming from the object, cataloged as SCP 06F6, also have eluded identification as being due to any specific element. One guess is that the features are redshifted molecular carbon absorption lines in a star roughly one billion light-years away. But searches through various astronomical survey catalogs for the source of the light have not uncovered any evidence for a star or galaxy at the location of the flash. The Supernova Cosmology Project at LBNL discovered it serendipitously in a search for supernovae. Hubble was aimed at a cluster of galaxies 8 billion light-years away in the spring constellation Bootes. But the mystery object could be anywhere in between, even in the halo of our own Milky Way galaxy. Papers published by other researchers since the event was reported in June 2006, have suggested a bizarre zoo of possibilities: the core collapse and explosion of a carbon rich star, a collision between a white dwarf and an asteroid, or the collision of a white dwarf with a black hole. But Barbary does not believe that any model offered so far fully explains the observations. "I don't think we really know what the discovery means until we can observe similar objects in the future." All-sky surveys for variable phenomena, such as those to be conducted with the planned Large Synoptic Survey Telescope, may ultimately find similar transient events in the universe. Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links SCP 06F6 at Wiki Stellar Chemistry, The Universe And All Within It
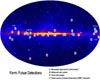 Greenbelt MD (SPX) Jan 08, 2009
Greenbelt MD (SPX) Jan 08, 2009NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has discovered 12 new gamma-ray-only pulsars and has detected gamma-ray pulses from 18 others. The finds are transforming our understanding of how these stellar cinders work. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |